DYNK
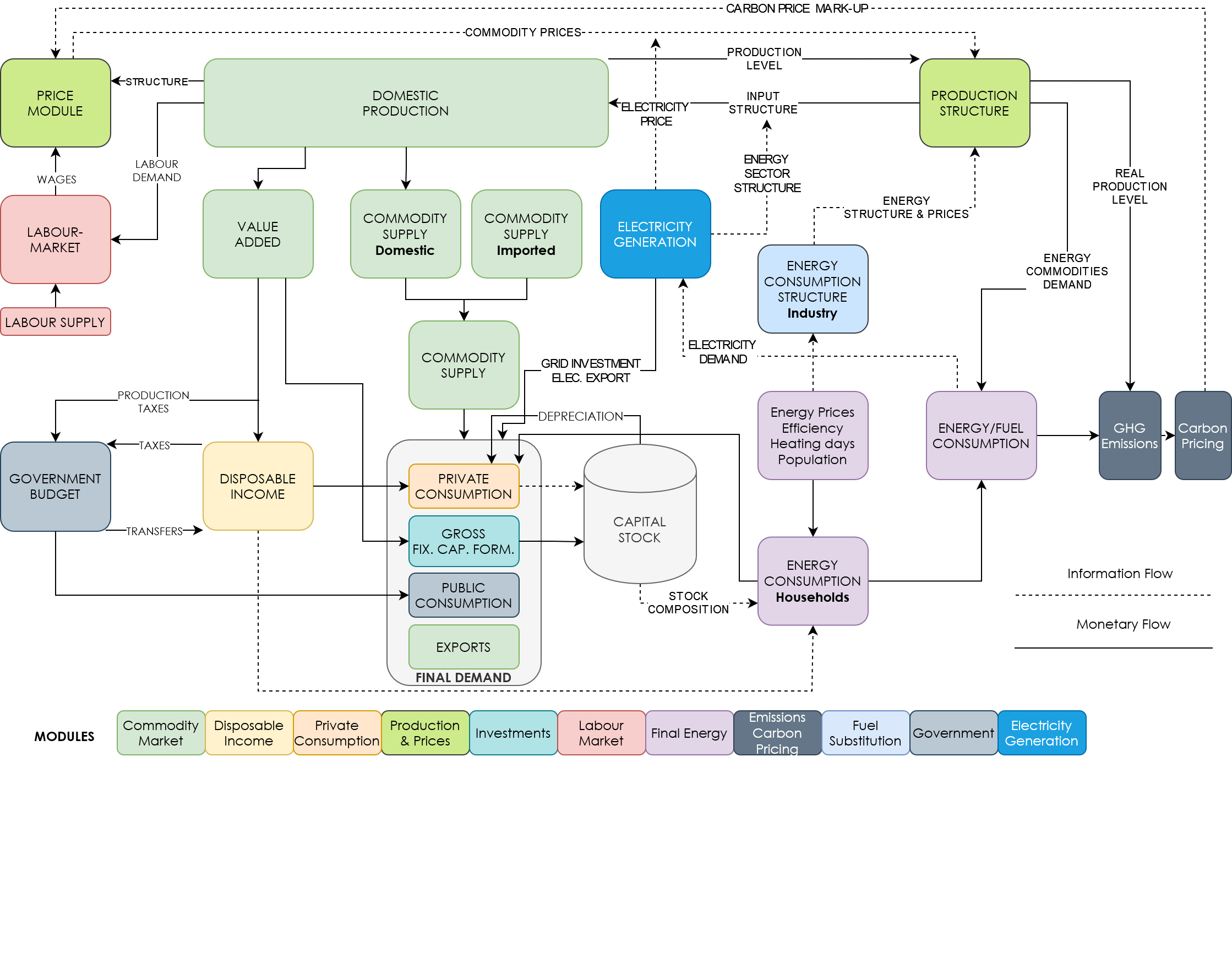
The DYNK (Dynamic New Keynesian) model is a hybrid between an econometric Input-Output (IO) and a CGE model. The model describes the interlinkages between 76 NACE industries as well as the consumption of different household types by 47 consumption categories (COICOP) and covers single-country economies (in this case, Austria). The term "New Keynesian" refers to the existence of a long-run full employment equilibrium, which – starting off from an unemployment equilibrium – will not be reached in the short run, due to institutional rigidities, this resembles features of a CGE model. The model has been extensively used for policy analysis (e.g. Kirchner et al. 2019, Sommer & Kratena 2019, or Kettner et al. 2024). Macroeconomic energy and environmental analyses, often with consideration of household characteristics, are the core focus of DYNK. We rely on the disaggregation of the energy supply sector (NACE sector 35) completed in the pre-project START2030 (Gaugl et al. , Kettner et al. 2023) for DYNK into three subsectors (electricity generation and distribution (35A), natural gas (35B) and district heat (35C) as a prerequisite for the analyses in Fair-Grid and for the linking with BALMOREL.
A detailed description of the DYNK model is provided e.g. in Kirchner et al. 2019.